Oculomotor Nucleus
The Common Vein Copyright 2010
Definition
The oculomotor nucleus is a collection of graymatter in the midbrain that is responsible for eye movement and functions with the Edinger Westphal nucleus to control pupillary constriction. It consists of a group of nuclii found in the anterior or ventral aspect of the peri-aqueductal gray and lies close to the aqueduct of Sylvius.
|
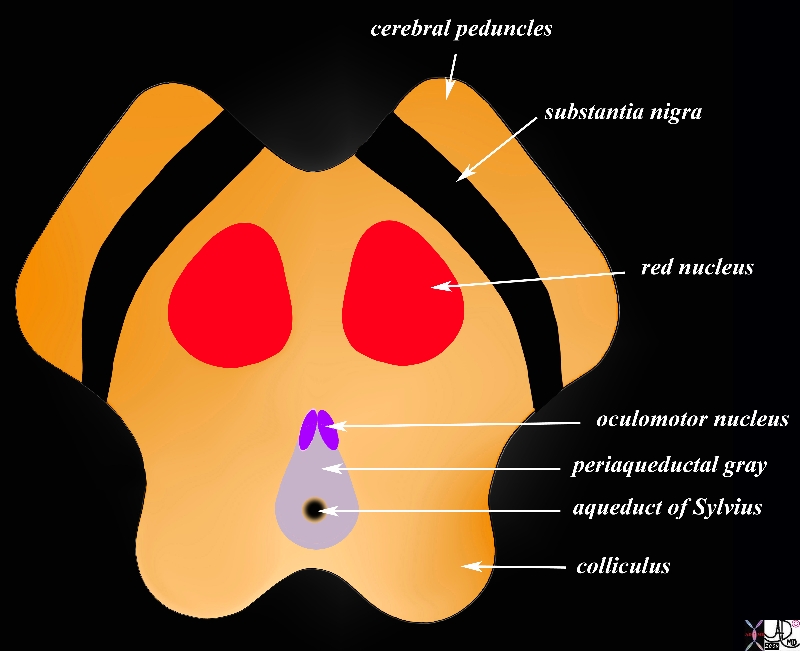
Cerebral Peduncles in Axial Projection |
|
The midbrain in transverse plane illustrates the component structures, with the image reminiscent of the face of a baby pig.. Anteriorly the cerebral peduncles are followed by the substantia nigra, and the collilculi The anterior border of the midbrain incorporates the cerebral peduncles, and the substantia nigra (black – just posterior to the peduncles). Between the substantia nigra and the aqueduct is an area of the midbrain called the tegmentum (floor of the midbrain) Within the tegmentum other structures include red nuclii, oculomotor nuclii, periaquaductal gray, and the aqueduct of Sylvius which is border forming between the tegmentum anteriorly and the tectum (roof) posteriorly. The posterior end of the midbrain is bordered by the colliculi in the tectum. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2010 all rights reserved 94074b08a06bL.9s |
|
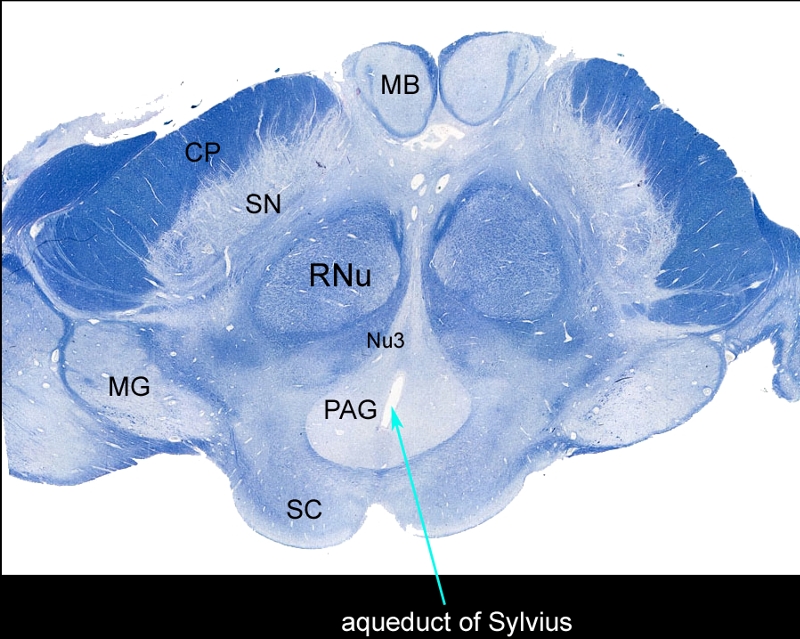
Whole Mount of the Midbrain in Axial Projection |
|
The mounted and stained midbrain in transverse plane illustrates the component structures. The anterior border of the midbrain incorporates the cerebral peduncles (CP), and the substantia nigra (SN). Between the substantia nigra and the aqueduct (teal arrow) is an area of the midbrain called the tegmentum (floor of the midbrain) Within the tegmentum other structures include red nuclii (RNu), oculomotor nucleus (Nu3), periaquaductal gray (PAG), and the aqueduct of Sylvius which is border forming between the tegmentum anteriorly and the tectum (roof) posteriorly. The posterior end of the midbrain is bordered by the colliculi in the tectum. Note also the paired mamillary bodies anteriorly (MB) and the medial geniculate body (MG) posterolaterally Courtesy Department of Anatomy and Neurobiology at Boston University School of Medicine Dr. Jennifer Luebke , and Dr. Douglas Rosene 98483L.8 |