The Common Vein Copyright 2010
Definition
The ventricular system is a complex fluid filled structure that enables cerebrospinal fluid to be secreted, stored and circulated in the brain and spinal cord.
Structurally it is diverse consisting of chambers that vary significantly in size, shape and position.
Its function is to store secreted CSF within its chambers and circulate the CSF into the subarachnoid spaces to bathe and protect the brain and spinal cord.
Diseases are most commnly cuased by mechanical obstructions whether by mass effect or by intrinsic stenosis. Normal pressure hydrocephalus is a relatively common condition of the elderly.
Diagnostic procedures are confined to MRI and CTscan which enable visualization of the ventricles and lumbar puncture which allows analysis of the pressures chemnical and cellular content of the CSF.
Treatment is often by shunt decompression o the ventricles
Components of the Ventricular System of the Brain |
|
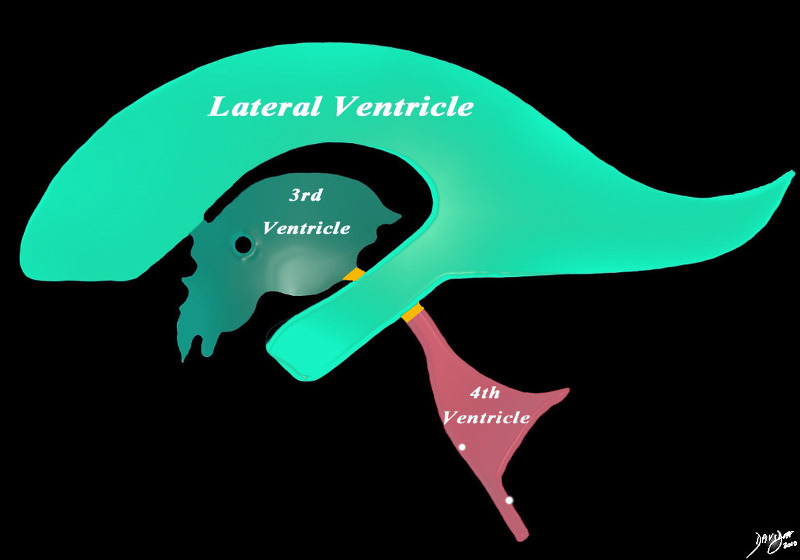
The diagram in the sagital projection reveals the anatomical distribution of the ventriclular components into the forebrain (green), midbrain (orange) and hindbrain (salmon). Courtesy Ashley DAvidoff MD copyright 2010 all rights reserved 94459b06b01.81s |
Components
It consists of ;
lateral ventricles (pair)
3rd ventricle
4th ventricle
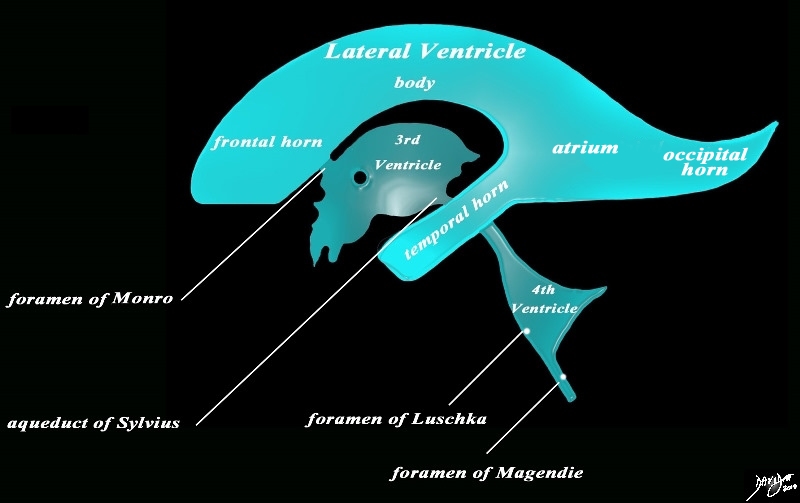
The lateral ventricles each consist of a frontal horn (anteriorly), body, and temporal horn
|
Detailed Components |
|
The diagram in the sagittal projection reveals the horizontal portion called the lateral ventricle. It is a paired structure that houses the frontal horn, body, and the vertical portion which is composed of the 3rd ventricle, cerebral aqueduct and the 4th ventricle. The lateral ventricle consists of the frontal horn, body, occipital horn, atrium and the temporal horn The foramen of Monro connects the lateral ventricles with the third ventricle. The paired foramina of Luschka are sitiuated anteriorly in the 4th ventricle and they allow CSF to circulate in the subarachnoid spaces. The foramen of Magendie is a single structure and is situated posteriorly and it also enables CSF to enter the subarachnoid space. code brain ventricles lateral ventricles frontal horn body occipital horn atrium temporal horn 3rd ventricle 4th ventricle foramen of Monro formamen of Magendie Foramen of Luschka anatomy normal neuroanatomy diagram conceptual diagram structure principles Davidoff Art Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2010 all rights Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2010 all rights reserved 94459b10b02.82s |
Connections
These structures connect via the;
The lateral ventricles connect with the 3rd ventricle via the foramina of Munro
The 3rd ventricle connects with the 4th ventricle via the aqueduct of Sylvius
The 4th ventricle connects with the subarachnoid space via the median aperture of Magendie
The 4th ventricle also connects with the subarachnoid spaces via paired foramina of Luschka
Position
The lateral ventricles are situated in the forebrain within the frontal parietal, occipital and temporal lobes
The 3rd ventricle is situated in the forbrain as well but the aqueduct of Sylvius is positioned in the midbrain.
The 4th ventricle is situated in the hindbrain posterior to the pons and medulla and anterior to the cerebellum.
|
The Recesses |
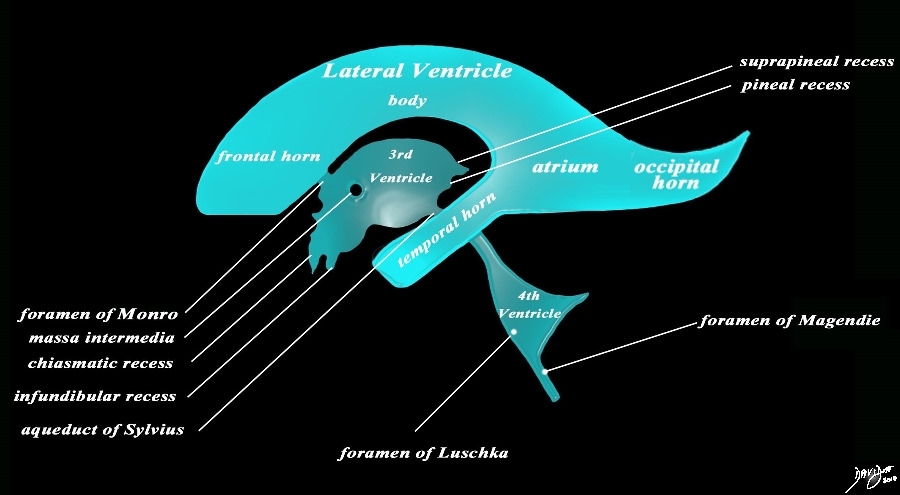
| The sagittal projection reveals the horizontal portion called the lateral ventricle. It is a paired structure, and houses the frontal horn, body, occipital horn and atrium. The vertical portion consists of the paired foramina of Monro, the midline third ventricle, the narrow aqueduct of Sylvius, the 4th ventricle the anteriorly placed paired foramina of Luschka, and the posteriorly positioned foramen of Magendie There are 4 recesses that create an unusual shape to the third ventricle. Anteriorly the chiasmatic (optic) recess lies above the infundibular recess. Posteriorly the suprapineal recess lies above the pineal recess. code brain ventricles lateral ventricles frontal horn body occipital horn atrium temporal horn 3rd ventricle 4th ventricle foramen of Luschka foramen of Magendie Foramen of Monro optic recess chiasmatic recess suprapineal recess pineal recess anatomy normal neuroanatomy diagram conceptual diagram structure principles Davidoff Art Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2010 all rights
Courtesy Ashley DAvidoff MD copyright 2010 all rights reserved 94459b14b.82s |