The Common Vein Copyright 2010
Introduction

The Circle of Willis |
|
The cerebral circulation has a unique system that allows for compensatory flow when any one of the 4 vessels is narrowed or occluded. This cerebral circulation is centered on the circle of Willis which has two basic systems that feed it; the carotid system (in this case salmon pink) and the vertebro-basilar system (brighter pink). They both feed into the circle of Willis (bright red) via communicating branches. The middle cerebral artery is the vessel that feeds into the COW by providing the anterior communicating artery and the posterior cerebral artery connects via the posterior communicating artery. Conceptually as depicted in this diagram the circle of Willis is the centre of the cerebral circulation and from it blood flows into the anterior (bright green), middle (darker green) and posterior cerebral (maroon) regions. Image Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2010 97194b09.8s |
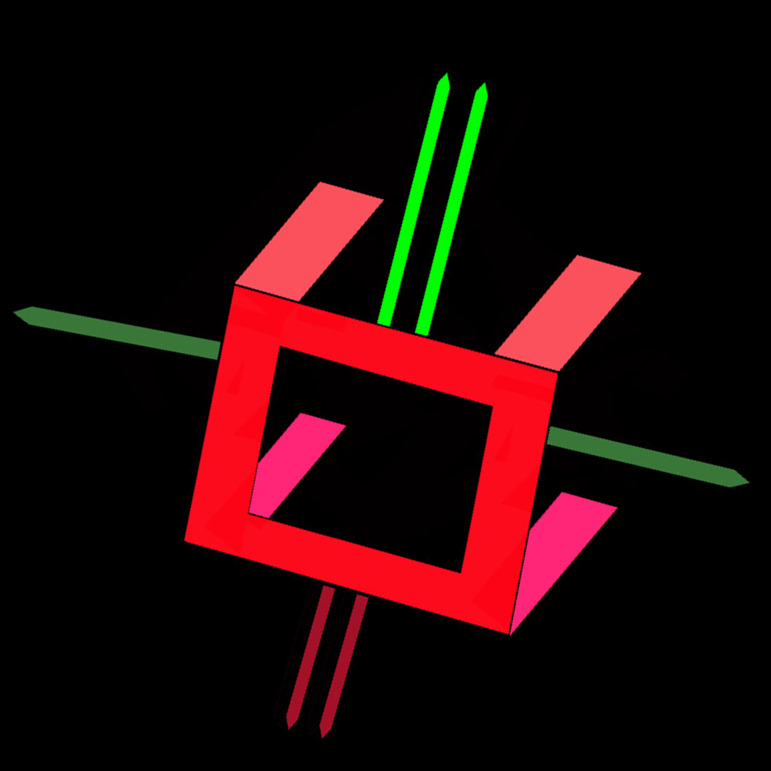
Branches To and From the Circle of Willis |
|
This cerebral circulation is centered on the circle of Willis which has two basic systems that feed it; the carotid system (in this case salmon pink) and the vertebro-basilar system (brighter pink). They both feed into the circle of Willis (bright red) via communicating branches. The middle cerebral artery is the vessel that feeds into the COW by providing the anterior communicating artery and the posterior cerebral artery connects via the posterior communicating artery. Conceptually as depicted in this diagram the circle of Willis is the centre of the cerebral circulation and from it blood flows into the anterior (bright green), middle (darker green) and posterior cerebral (maroon) regions. Image Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2010 97194b16b.8s |
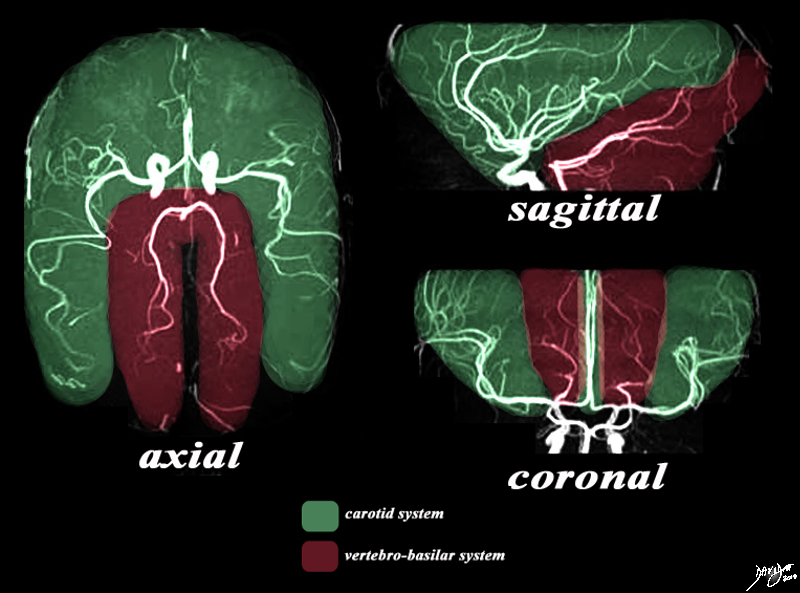
The Two Systems – Carotid and Vertebrobasilar |
|
There are two systems that supply the brain with blood. The MRA depicted in the axial, sagittal, and coronal views depict the general areas covered by the two systems. The carotid system gives rise to the anterior and middle cerebral arteries which cover the green area. The vertebro-basilar system, mostly through the posterior cerebral artery and cerebellar arteries, supply the maroon portion. Image Courtesy Philips Medical Systems Artistic rendering Davidoff MD Copyright 2010 92479c03.8s |
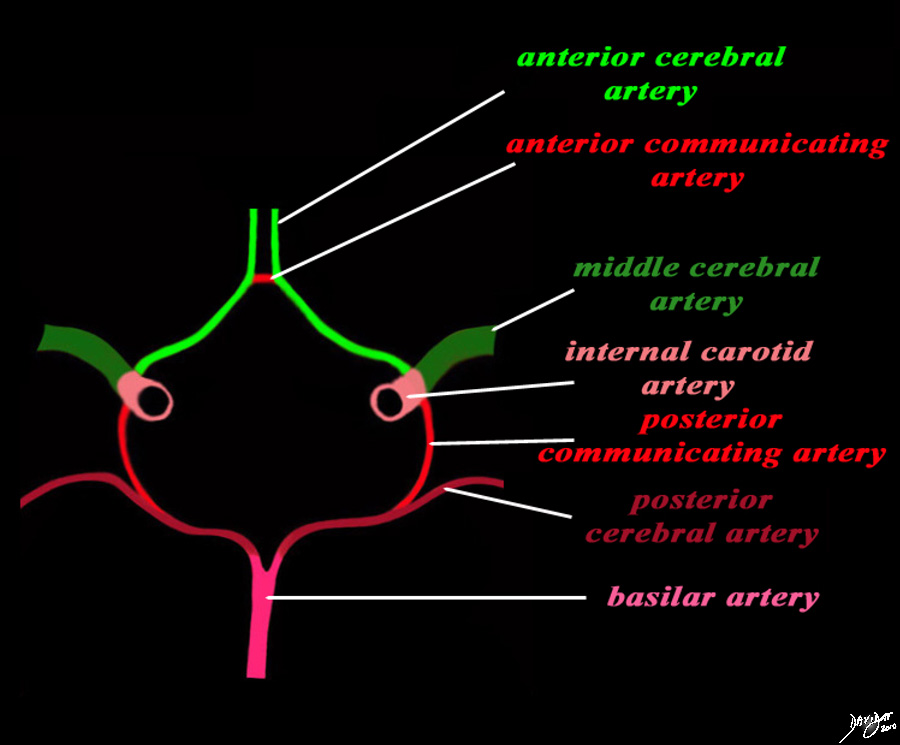
Structures of the Circle of Willis |
|
The diagram shows the main branches of the blood supply to the brain which includes the carotid and vertebro-basilar systems. These are the vessels that particpate in the formationofthe circle of Willis The carotid system supplies the brain from the internal carotid (salmon pink) – a branch of the common carotid which arises from the aorta. Its terminal bifuracation into the middle cerebral (dark green) and anterior green (bright green) are shown. The anterior communicating artery runs between the two anterior cerebrals (bright red) The basilar artery (pink) is formed by the two vertebral arteries and travel as a single artery over the upper medulla and the entire pons. Its terminal branch is the posterior cerebral artery (maroon). Each of the vessels contributes to the circle of Willis through communicating arteries. The vertebro-basilar system provides the posterior communicating arteries bilaterally and the carotid system provides the anterior communicating arteries via the anterior cerebral artery. code brain Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2010 All rights reserved 97194b13g04L01.91s |
|
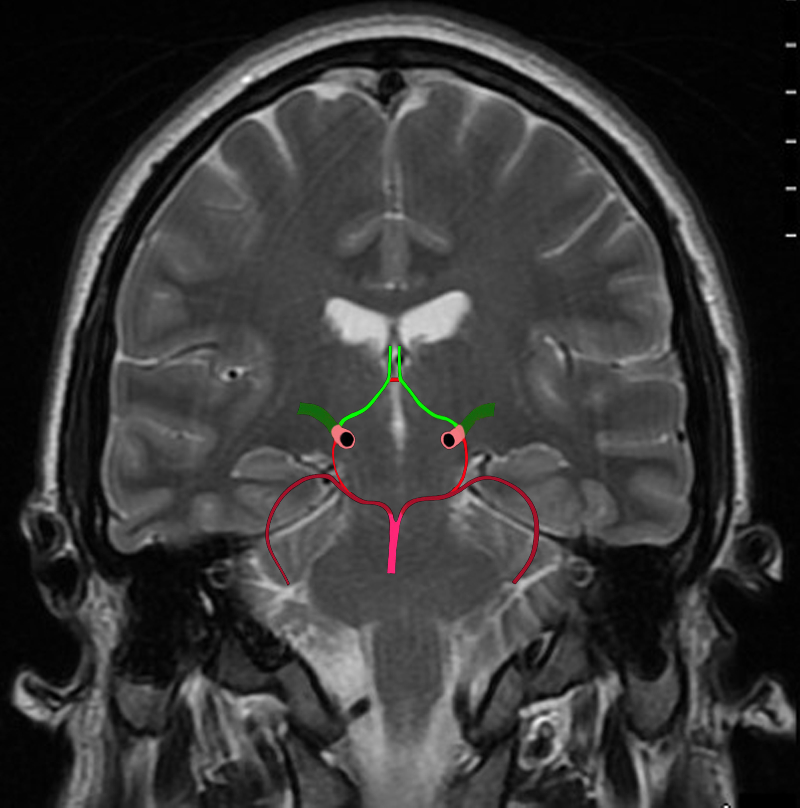
The Circle of Willis Overlaid on a Coronal View of the Brain |
|
The diagram shows the main branches of the blood supply to the brain including the circle of Willis overlaid on coronal MRI image to portray the approximate position of the vessels in the brain. The carotid system supplies the brain from the internal carotid we demonstrate its terminal bifurcation into middle cerebral (dark green) and anterior cerebral (bright green). The anterior communicating artery runs between the two anterior cerebrals (bright red) The basilar artery (pink) is formed by the two vertebral arteries and it travels as a single artery over the upper medulla and the pons. Its terminal branch is the posterior cerebral artery (maroon). Each of the carotid and vertebro-basilar systems contributes to the circle of Willis through communicating arteries. The vertebro-basilar system provides the posterior communicating arteries bilaterally from the posterior cerebral and the carotid system provides the anterior communicating arteries via the anterior cerebral arteries. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2010 All rights reserved 89721c06b.8sg04.8s |
|
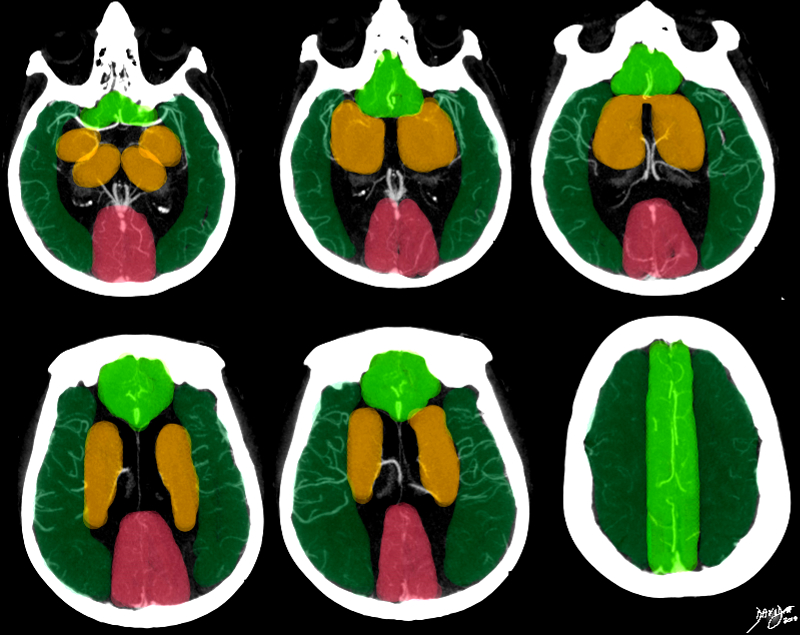
Segmental Blood Supply |
|
This series of axial images is from a CTA of the cerebral circulation and shows the middle cerebral artery at its origin and its major branching pattern exemplified by the vessels branching in the Sylvian fissure to the frontal, temporal, and parietal lobes. The branches of the MCA have been overlaid in red, and the approximate territory perfused by these vessels overlaid in dark green. The anterior cerebrl regions are overlaid in bright green and the regions of the posterior cerebral artery overlaid in salmon pink. The basal ganglia and thalamus are outline in orange and they receive most of their blood supply from the middle cerebral artery, but they are relatively hypovascular compared to the cortex. Image Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2010 76500c02b.8s |