Forebrain
Transverse View
Concepts
The Common Vein
Copyright 2010
The Parts, The Gray Matter and the White Matter
The forebrain is divided into the frontal, parietal and occipital lobes based on fissural anatomy and functional anatomy. Within the lobes there is a microcosm of structures that and fibres that cross these boundaries. Conceptually we approach this much like a map of the world defining continents and countries by artificial borders but the ebb and flow of activity between continents is one continuous integrated structure
We start with the basic structure of the brain map – frontal lobes, parietal lobes, occipital lobes and temporal lobes
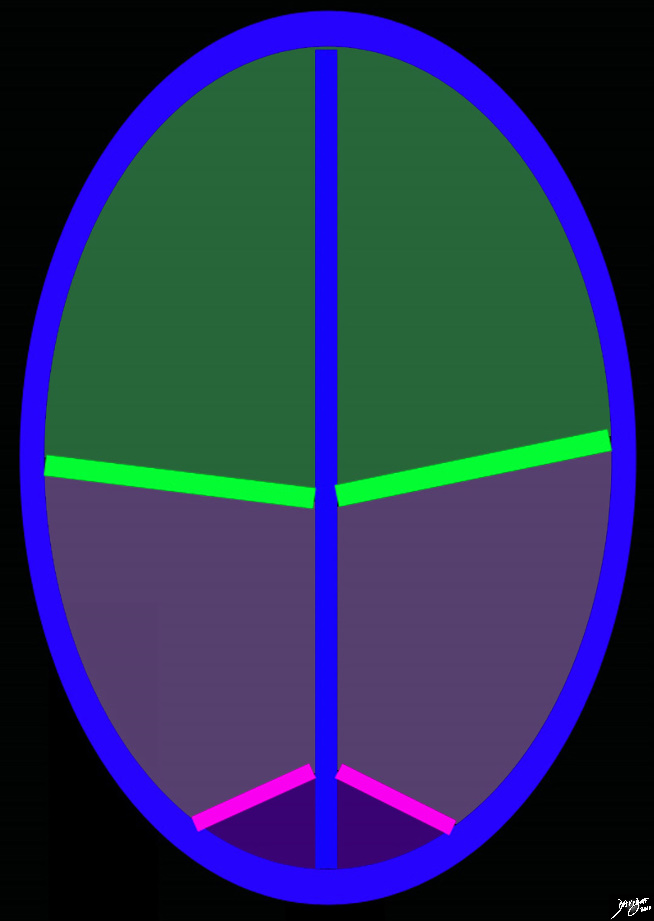
Frontal Lobe Parietal Lobe and Occipital Lobe Central Sulcus and PArito-occipital Sulcus |
|
The diagram reflects the interhemispheric fissure as depicted in the axial plane dividing the brain into two halves. The bright green line represents the central sulcus which separates the the frontal lobes (green) from the parietal lobes (light purple. The parito-occipital fissure (pink) separates the parietal lobes from the occipital lobes. By convention anterior is on the top and posterior on the bottom, while the patients right is to our left and vice versa for the patients left brain Copyright 2010 Courtesy Ash;ley Davidoff MD 93914.85sb |
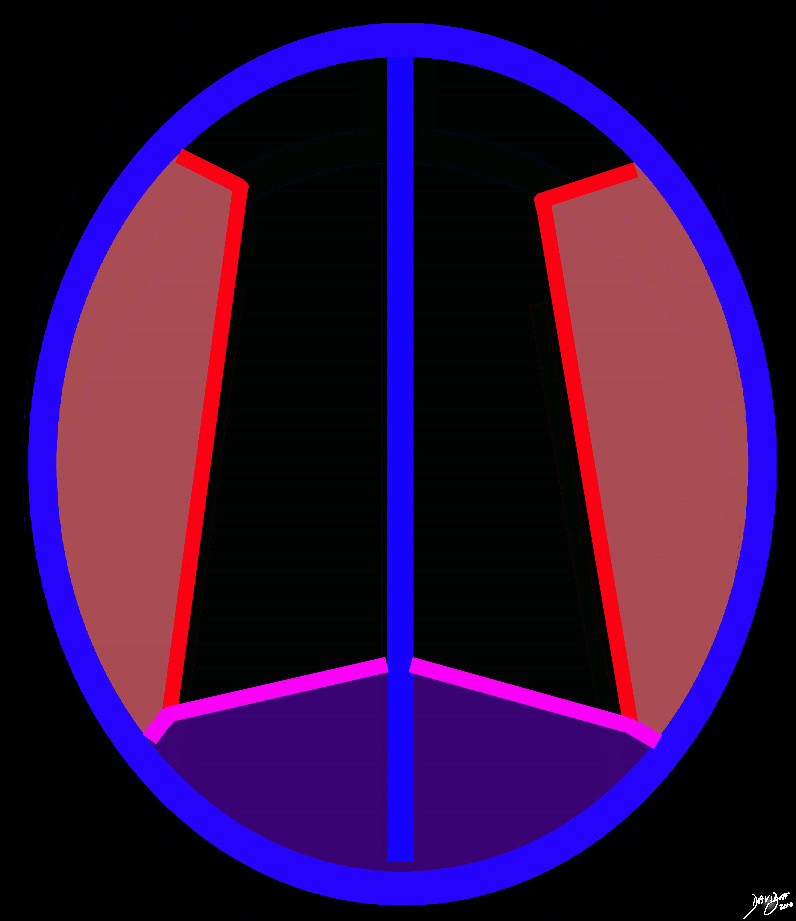
Level of the Occipital and Temporal Lobes |
|
At a lower level the parietooccipital fissure (pink) defines the anterior edge of the occipital lobe posteriorly (purple). The Sylvian fissure (bright red lines) defines the temporal lobes (light red) Copyright 2010 all rights reserved 93914.36k.81s |
The stricuture that cross the borders without the knowledge of the borders defined above take on the abstracted shape of inverted C’s around the midline as conceptualised by the diagram below.
|
Backward C’s of the Forebrain Structures |
|
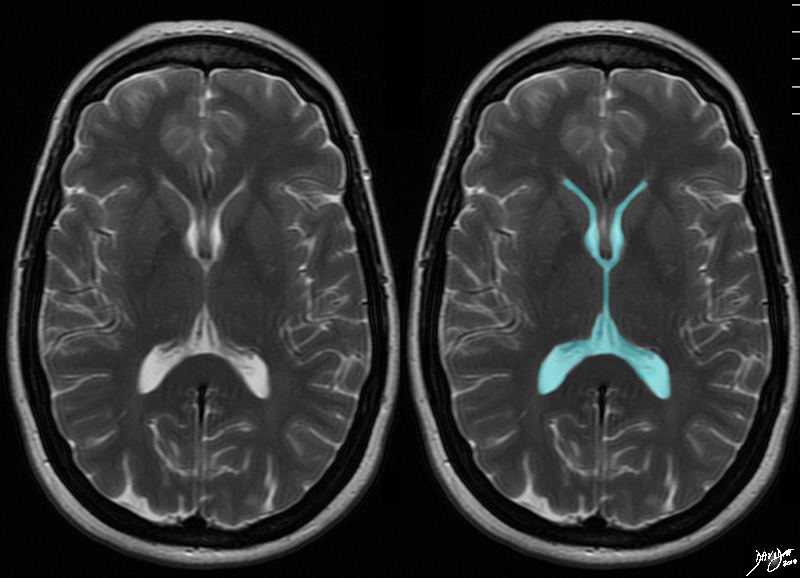
The initial approach to the axial images as we proceed deeper into the brain, and particulalrly the forebrain in this instance, is a series of back to front bilateral c’s, the shape of which is set by the lateral ventricles Davidoff art Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2010 93914.3ka09.8s |
|
The Most Medial Layer – The Ventricles |
|
At this level through the large portion of the ventriclesthe bilateral backward “C’s are composed of the ventricles themselves. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2010 all rights reserved 94079cd01.8s |
|
Paraventricular Structures |
|
The layer after the ventricles are supraventricular and paraventricular structures. The paraventricular structures in general conform to the axis of the lateral ventricles superiorly, and are color coded in orange Davidoff Art Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2010 all rights reserved 93914.3ka04b01.8s |
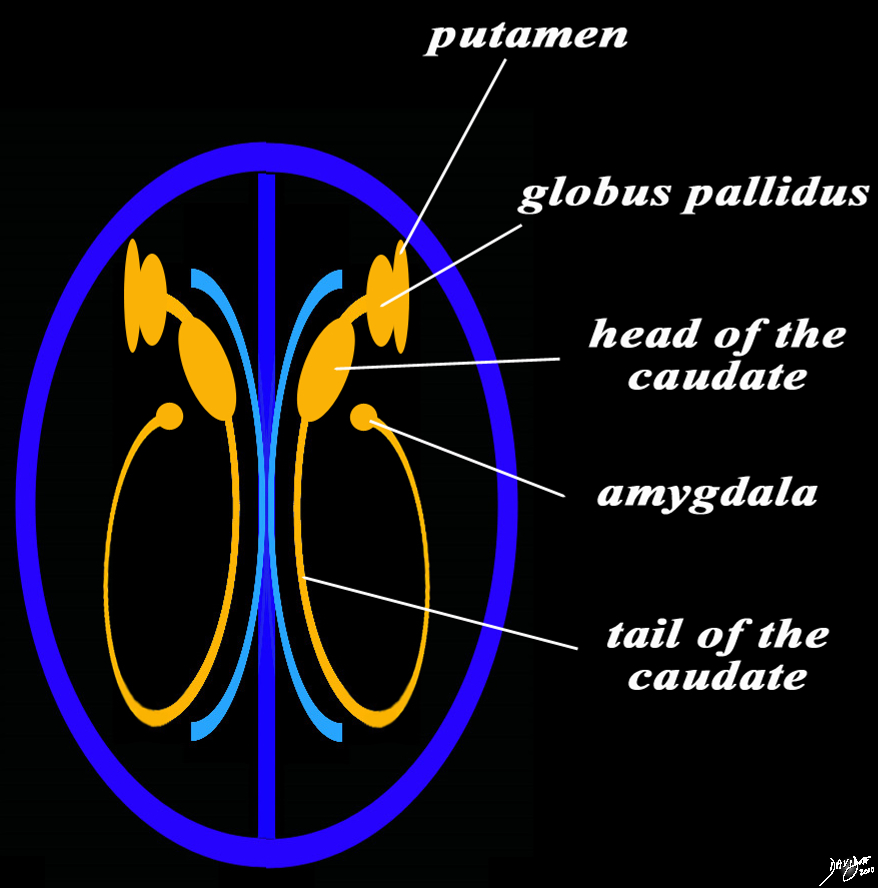
The Basal Ganglia |
|
The basal ganglia in the forebrain in the axial projection are seen as a continuous inverted C as well. In this diagram their relationship to the ventricles distributed in paraventricular fashion is exemplified. In the conceptual diagrams we have colored the inverted “C” that abuts the ventricular system orange, and this includes the putamen, globus pallidus, head of the caudate nucleus, tail of the caudate nucleus and the amygdala. The amygdala appears to be part of the limbic system and the basal ganglia. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2010 All rights reserved 93914.3ka04b01e05.8s |
|
The Thalami |
|
More posteriorly but remaining in the paraventricular plane is the larger thalamus Davidoff art Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2010 all rights reserved 93914.3ka04b01b02.8s |
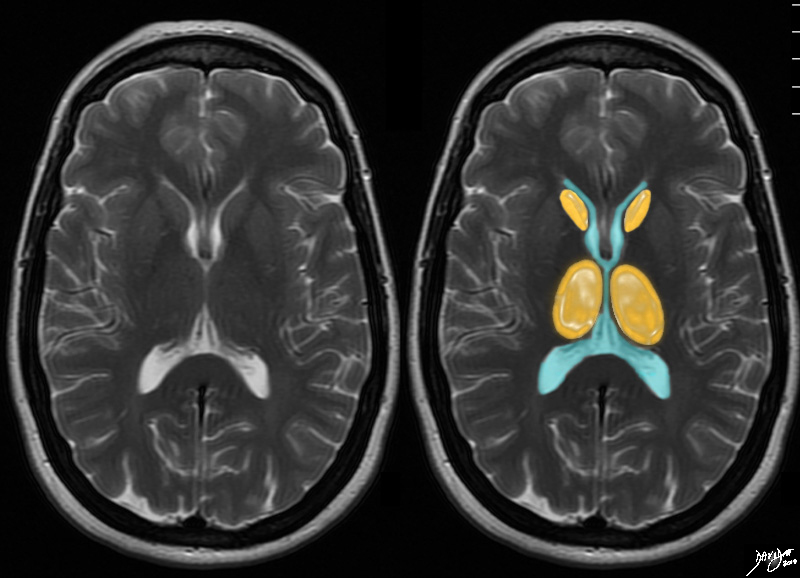 The Orange Layer The Orange Layer
Caudate Nuclii and Thalami |
|
The axial T2 weighted MRI is taken through the level of the ventricles. The next outward layer is an orange layer and at this level it represents the caudate nuclii anteriorly and the thalami posteriorly Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2010 all rights reserved 94079cd05.8s |
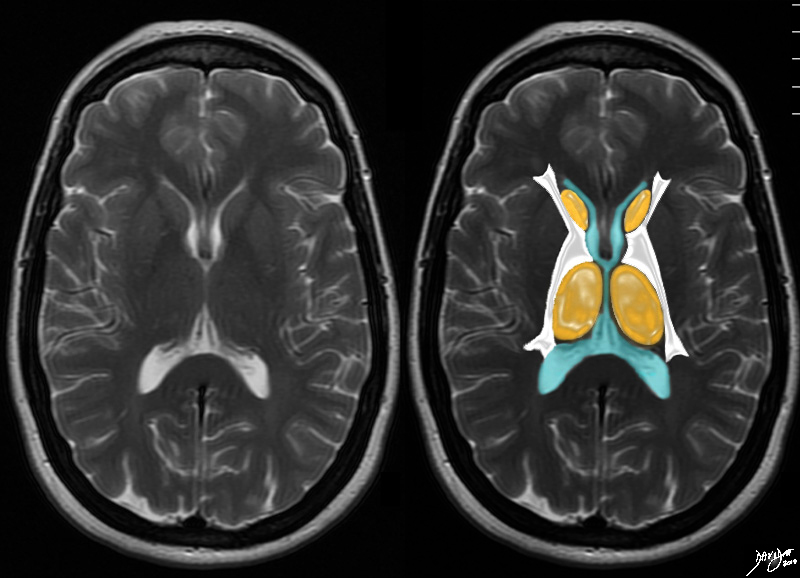 The White Matter LAyer The White Matter LAyer
The Internal Capsule |
|
The axial T2 weighted MRI is taken through the level of the ventricles. The next outward layer is a white matter layer and at this level it represents the internal capsule Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2010 all rights reserved 94079cd06b01.81s |
|
Adding the Putamen |
|
The axial T2 weighted MRI is taken through the level of the ventricles. It demonstrates the midline ventricuar system, the and the orange ring of paraventricuar basal gaglia including tye caudate nuclii (most anterior and medial) the and the putaen. It also demonstrates putamen which is a pink slmomn in color lying lateral to the white matter. The thalami ar noted posteriorly. The body of the corpus callosum is above this level. The most anterior portion of the corpus callosum and most posterior portion are seen at this lower level of the ventricles Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2010 all rights reserved 94079cd07b.81sh |
|
Gray Matter on the Outside |
|
On the periphery of the brain is the gray matter, which is where thethe highest functions of the brain originate. Davidoff art Courtesy Ashley Davidoff copyright 2010 all rights reserved 93914.3ka12.8s |
|
Add the White Matter |
|
The White matter is the transport system between the gray matter and all parts of the brain and sppinal cord and eventaully as nerves to the end organs, often via complex pathways Davidoff art Courtesy Ashley Davidoff copyright 2010 all rights reserved 93914.3ka13.8s |